How Did White Women Who Worked In Service-sector Industries Fare During The Great Depression?

Whether you're having surgery, undergoing tests or have other medical needs involving your bladder, your medico may need to insert a catheter to assist in your diagnosis or handling processes. A catheter is a device that's inserted into your bladder to bleed urine out of your body so it can then exist collected for testing or disposed of. If you or a loved 1 need to undergo catheterization, learning more than near what's involved, forth with some other of import information related to catheterization for women, can help you lot feel more confident about and amend prepared for the procedure.
What Are Catheters?
Catheters are simple devices; one of the almost common, called a Foley catheter, consists of a hollow tube, a small airship, a port and a drainage handbag. The small-scale balloon is situated on one end of the tube. This end is inserted up through a patient'due south urethra — which is the pocket-size aqueduct that moves urine from the bladder to the outside of a person'south body — and into her float. The balloon is then inflated with sterile water, which holds the catheter tube in place and prevents leakage. The port section splits the inserted portion of the tube into 2 separate tubes, ane of which directs urine into the drainage pocketbook. The other tube section allows for inflation and deflation of the airship.
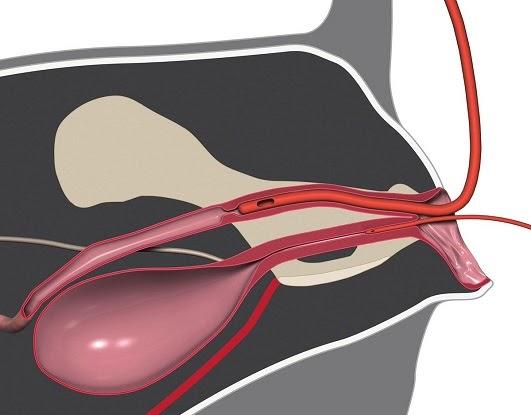
A Foley catheter is a blazon of indwelling catheter. "Indwelling" means that the catheter remains inside the urethra and float for a curt or long menses of time, such every bit days or weeks, without removal. These types of catheters are generally used for managing long-term wellness conditions, such as urinary incontinence or an inability to urinate. Doctors also typically use indwelling catheters for people who are bedridden or unconscious due to conditions like a coma or because they're under full general anesthesia.
Another blazon of catheter insertion is called make clean intermittent catheterization, or CIC. In this type of catheterization, the catheter doesn't remain in the bladder and urethra and it also doesn't have a balloon on the end. Instead, the catheter tube is inserted briefly — just long plenty for the patient'southward bladder to bleed — then removed immediately. Medical professionals may perform CIC to obtain sterile urine samples from patients who have problem urinating or to mensurate a person'southward urine output. Women who've had certain gynecologic surgeries may as well opt to perform CIC on themselves if they're unable to empty their bladders post-obit those procedures.
How Practice Doctors Insert Catheters?
The method of insertion for a catheter depends on the type of catheterization that you need. If you're having an indwelling catheter placed, during your appointment you'll remove vesture from the lower half of your body. You'll need to lie flat, bend your knees and spread your legs so the clinician can access your urethra. They'll then carve up your labia to clean your urethral opening and the surface area around it. Following this, the clinician will use a polish-tipped syringe to inject a small amount of lubricant into your urethra. This makes information technology easier for the catheter tubing to slide upwardly to your bladder.

One time this prepping is consummate, the clinician volition begin gently sliding the clean catheter up through your urethra until it reaches your bladder and urine begins flowing out. They'll inflate the airship to concord the catheter in place and, if they haven't yet, attach the drainage bag to the open end of the catheter tubing. You'll wear and empty this purse (or replacement bags) until you have the catheter removed. Most people who wearable indwelling catheters secure the bags to their legs so gravity helps the urine accomplish and stay in the purse. If you're having the catheter inserted for surgery, the doctor may await until you're already under anesthesia to identify the device.
The process for placing an intermittent catheter is similar to that for the indwelling catheter. A clinician cleans around your urethra and lubricates it before placing the catheter tubing. After this, they can collect a urine sample and remove the catheter tubing. People as well self-catheterize using CIC if they're unable to void urine on their own or if they need to track their urine output for medical reasons. The process and the position your torso is in may be somewhat unlike if you apply CIC at home — some people sit on the toilet and perform CIC to bleed their urine — and your physician tin prove you the proper technique to use in this situation.
Are There Whatsoever Risks With Catheterization?
Catheterization is a relatively simple process — and i that'due south common — simply at that place are a few risks associated with having a catheter inserted. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most mutual trouble for people who have indwelling catheters, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine. This tin happen if the catheter isn't sterilized properly earlier insertion. If bacteria remain on the catheter when information technology'southward placed into your float, this can innovate the leaner into your float, where they brainstorm multiplying — resulting in infection.

After you've had an indwelling catheter placed, information technology'due south important to exist on the lookout for changes in your urine's odor, amount and advent. With a UTI, y'all might notice that your urine smells bad or has a much stronger odor than usual. Your urine might also look cloudy or thick, and you may notice blood in information technology. The amount of urine collecting in the drainage handbag may lessen even when you're still drinking fluids.
Other UTI signs and symptoms to look out for include a fever, hurting in your abdomen or lower back, chills, aches, discharge leaking effectually your urethra where the tube comes out and general fatigue. If you notice any of these symptoms after your catheter insertion, call your dr. immediately. They tin can remove the catheter and give you antibiotics to help clear up the infection.
Insertion of a catheter tin also cause damage to your urethra and to your bladder. Although it's very rare, sometimes a catheter tube tin puncture a person'south bladder wall. If you have any questions or concerns about using or maintaining your catheter — or if y'all're experiencing pain subsequently having it placed — don't hesitate to phone call your dr. for assistance.
Resource Links:
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003981.htm
https://www.hcd.com/urology/foley-catheter/
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000140.htm
https://www.med.uottawa.ca/procedures/ucath/
https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/uti/CA-UTI_tagged.pdf
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000483.htm
https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2865895/
Source: https://www.symptomfind.com/healthy-living/catheterization-for-women?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740013%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex
Posted by: walshthowelf1956.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Did White Women Who Worked In Service-sector Industries Fare During The Great Depression?"
Post a Comment